
Greenhouse gasses, Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a naturally occurring gas in Earth’s atmosphere. It is also produced by burning fossil fuels and is responsible for about 60% of the greenhouse effect, which keeps our planet warm enough to support life as we know it. Carbon dioxide is produced by all animals, including humans; it forms when animals breathe out oxygen and break down food to make energy. Plants also release carbon dioxide when they use sunlight to convert water into sugars through photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide has no color or odor, but it does have an important role in maintaining our climate: When CO2 levels rise in the atmosphere, they allow more heat from our sun to reach Earth’s surface—and that causes global temperatures to go up too!
what are greenhouse gasses
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are a group of gasses that make up the Earth’s atmosphere. The primary greenhouse gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide, both of which occur naturally in the atmosphere. Other GHGs include methane and nitrous oxide, which can be produced by humans through activities like agriculture and fossil fuel combustion.
The primary role of GHGs is to trap heat on Earth, making it habitable for life as we know it by keeping temperatures from getting too cold and from getting too hot. However, since the Industrial Revolution began in the 18th century and human activities began producing more carbon dioxide than ever before, concentrations of this key GHG have increased substantially: CO2 levels grew from 280 ppm during preindustrial times to 400 ppm today—a rise of over 45 percent!
greenhouse gases definition
Greenhouse gases are gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases are naturally produced by the earth, but human activity is increasing their amount in our atmosphere and causing global warming.
greenhouse gasses emissions
When it comes to greenhouse gasses, the most important thing to remember is that human beings are responsible for emitting them into the atmosphere. There are three main types of greenhouse gases (GHGs): carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O). The concentration of these gases in our atmosphere has increased over the past 200 years as a result of industrialisation and the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, oil and wood.
what do greenhouse gasses do
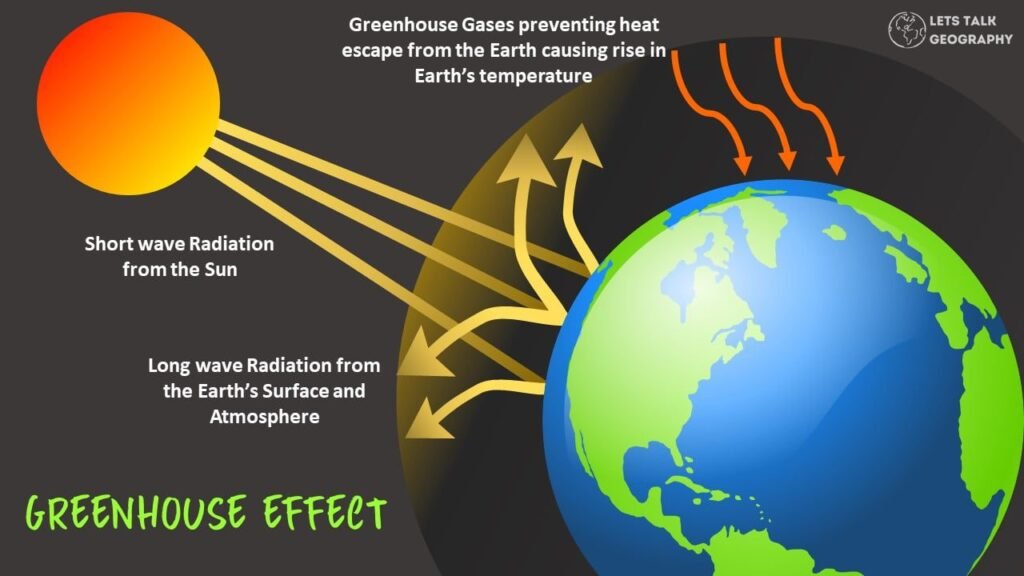
The greenhouse effect is the process by which gasses in Earth’s atmosphere trap heat and prevent it from escaping into space. The gases we’re talking about are carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane, which are released when we burn fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
This process has been going on for thousands of years—and we’ve just recently started adding so much CO2 to the atmosphere that it’s having a noticeable impact on our climate system. Carbon dioxide is naturally present in our atmosphere: plants use photosynthesis to grow and produce oxygen; they also need carbon dioxide to do this, which they absorb from the air around them through tiny pores in their leaves called stomata (Greek for “mouth”).
It’s important not only because it helps plants grow but also because it helps keep us warm: without abundant CO2 in our atmosphere trapping heat from escaping into space every night while we sleep under blankets or quilts made from wool grown by sheep who graze freely over miles upon miles of land owned by farmers who once had large families where each child could learn how hard work could be done without being distracted by technology until one day when two sisters named Eva took over their father’s farm business with different ideas about how things should be run than their mother did
what is greenhouse gasses
Greenhouse gasses are a group of gases that make up the Earth’s atmosphere. They help hold in heat and trap it on the planet, making life possible. Without greenhouse gasses, temperatures would drop to freezing or even colder.
Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities. In either case, these gases contribute to climate change by trapping heat in our atmosphere instead of allowing it to escape into space as radiation.
why are greenhouse gasses bad
Greenhouse gasses are bad for the environment. They contribute to climate change, smog and acid rain. Greenhouse gasses also cause global warming and contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer.

Methane
Methane is a greenhouse gas. It’s produced by the decomposition of organic matter, like dead plants and animals. This process happens naturally in the environment without humans being involved—but some of it is produced because we’re taking over land that would otherwise be occupied by wildlife, and we grow crops on it instead. Other sources of methane include animal digestion (hello cows!), bacterial fermentation in our own guts when we digest food (eep), volcanoes, farts and belches from ruminants such as cows and sheep… Did I miss anything?
It may not be intuitive how these various sources add up: after all, if there are no cows around to produce dung or burp methane out their noses then surely there wouldn’t be any at all! But don’t worry—if you look up enough facts about the world around you then eventually something will click into place!
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide (N 2 O) is a gas that occurs naturally in the atmosphere, but it is also emitted into the atmosphere by human activities such as agriculture and fossil fuel burning.
Nitrous oxide has an atmospheric lifetime of about 120 years. When released into the atmosphere, nitrous oxide can be oxidized to a stable form that contributes to stratospheric ozone depletion.
Ozone
- Ozone is a gas that is naturally present in the atmosphere.
- Ozone is created by the reaction of sunlight with other chemicals in the atmosphere, which forms ozone when it reaches ground level.
- Ozone can cause health problems and damage crops at ground level, so it’s important to keep an eye on ozone levels and make sure they’re not too high!
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are a group of chemicals used in air conditioners and refrigerators, as well as in aerosol propellants. CFCs have been replaced by other substances that do not harm the ozone layer, but their long lifetime means that they will persist for decades to centuries.
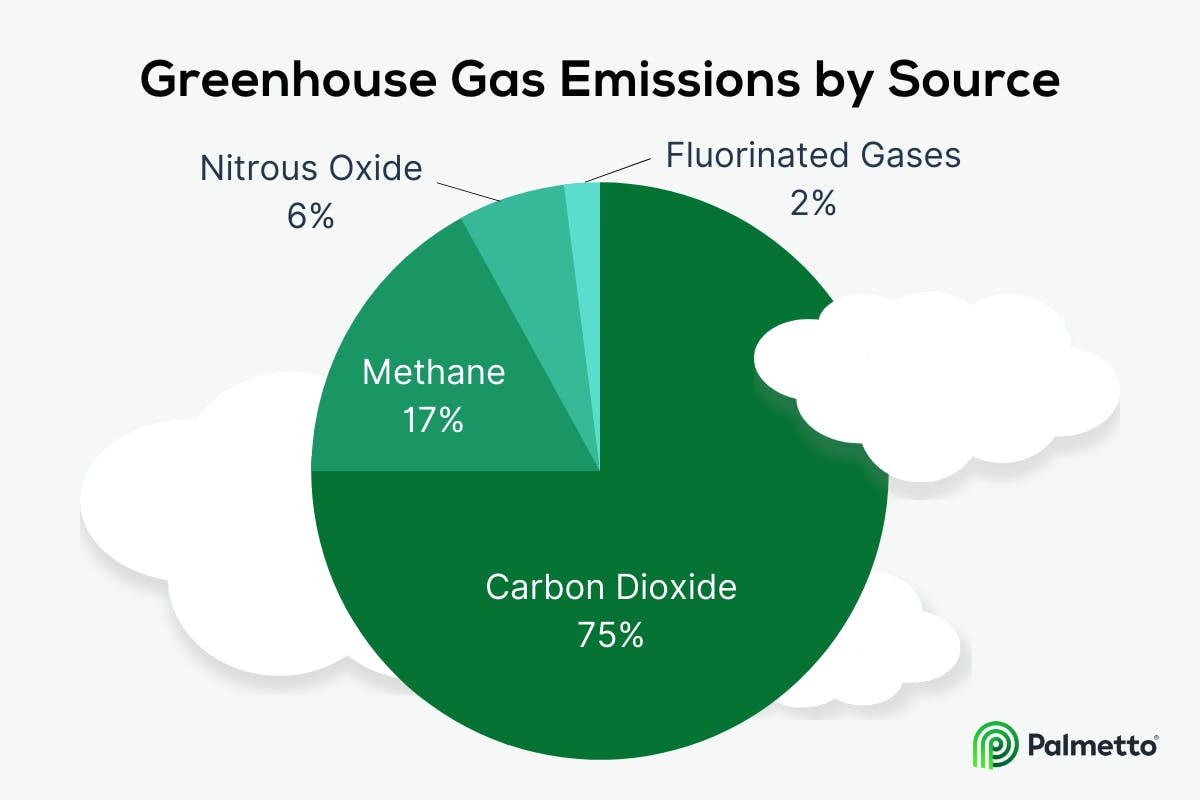
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and CFCs are the five main greenhouse gasses.
The most abundant greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide and it’s produced through burning of fossil fuels, deforestation and cement production. It’s also released by animals when they exhale CO2 as part of their respiration process. Carbon dioxide makes up 60-80% of the total amount of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere.
Methane is produced by livestock, rice paddies and landfills. The concentration of methane in our atmosphere has increased over 20% since 1750 and continues to rise at a rate that scientists call “alarming” – it will be 90 times greater than pre-industrial levels by 2100 if current trends continue!
Greenhouse gasses are a group of gasses that make up the Earth’s atmosphere.
Greenhouse gasses are a group of gasses that make up the Earth’s atmosphere. They trap heat in the atmosphere and keep our planet warm enough for life to survive. The greenhouse effect is a natural part of Earth’s environment, but when there are more greenhouse gasses than usual, it leads to global warming. There are five main greenhouse gasses: carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3) and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
Greenhouse gasses trap heat on the planet.
Greenhouse gasses are a natural part of the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, keeping the planet warm enough to support life. Without greenhouse gases, Earth would be too cold for life as we know it.
However, too much of a good thing can be bad for you. Too much CO2 in your diet can make you sick; too much CO2 in our atmosphere causes global climate change—specifically an increase in average temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns worldwide—which could have devastating effects on plant and animal species across the globe
Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities.
Natural greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide. These gases occur naturally in the atmosphere and are vital to life on Earth. For example, carbon dioxide is a major source of energy for most plants that produce oxygen during photosynthesis. Greenhouse gases also keep our planet warm enough to support life by preventing solar radiation from escaping into space. Without this natural greenhouse gas process, Earth would be much colder than it is today.

Naturally occurring greenhouse gases have been part of Earth’s atmosphere for centuries.
Greenhouse gases are the main cause of global warming. Most of these gases are natural and occur in the atmosphere naturally. These include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and CFCs. Some greenhouse gases are man-made and result from human activities such as burning fossil fuels (coal and oil), burning trees to make paper products, using fertilizers on agricultural crops, etc.
The name greenhouse gas stems from their ability to trap solar energy just like a greenhouse does.
The name greenhouse gas stems from their ability to trap solar energy just like a greenhouse does. Greenhouse gases are a group of gasses that make up the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases trap heat on the planet, which keeps our climate stable and habitable for life as we know it. Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities.
These are all of the greenhouse gases
Here are all of the greenhouse gases:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
- Ozone (O3) – This is the same stuff that protects us from UV radiation and gives us “good” sunburns. It’s a natural byproduct of atmospheric reactions involving sunlight, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. In the stratosphere ozone blocks most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays; in lower atmosphere it can be harmful to human health and damage plant life. When tropospheric ozone forms it has an adverse effect on crops and causes people to become sick if they are exposed to high levels of ozone for long periods of time. Tropospheric ozone also damages trees directly by causing stress response mechanisms in plants which leads them not being able to grow properly because they’re so busy dealing with this new threat!
Conclusion
We hope this article helped you understand what greenhouse gasses are, their definition and why they’re important for our planet. We also explained how these gases are produced by natural processes as well as human activities like burning fossil fuels.
Read More : Haunted house restaurant ohio








